Waste Heat Recovery Systems on a Wind Turbine Installation Vessel
Written by: Jeroen Berger •
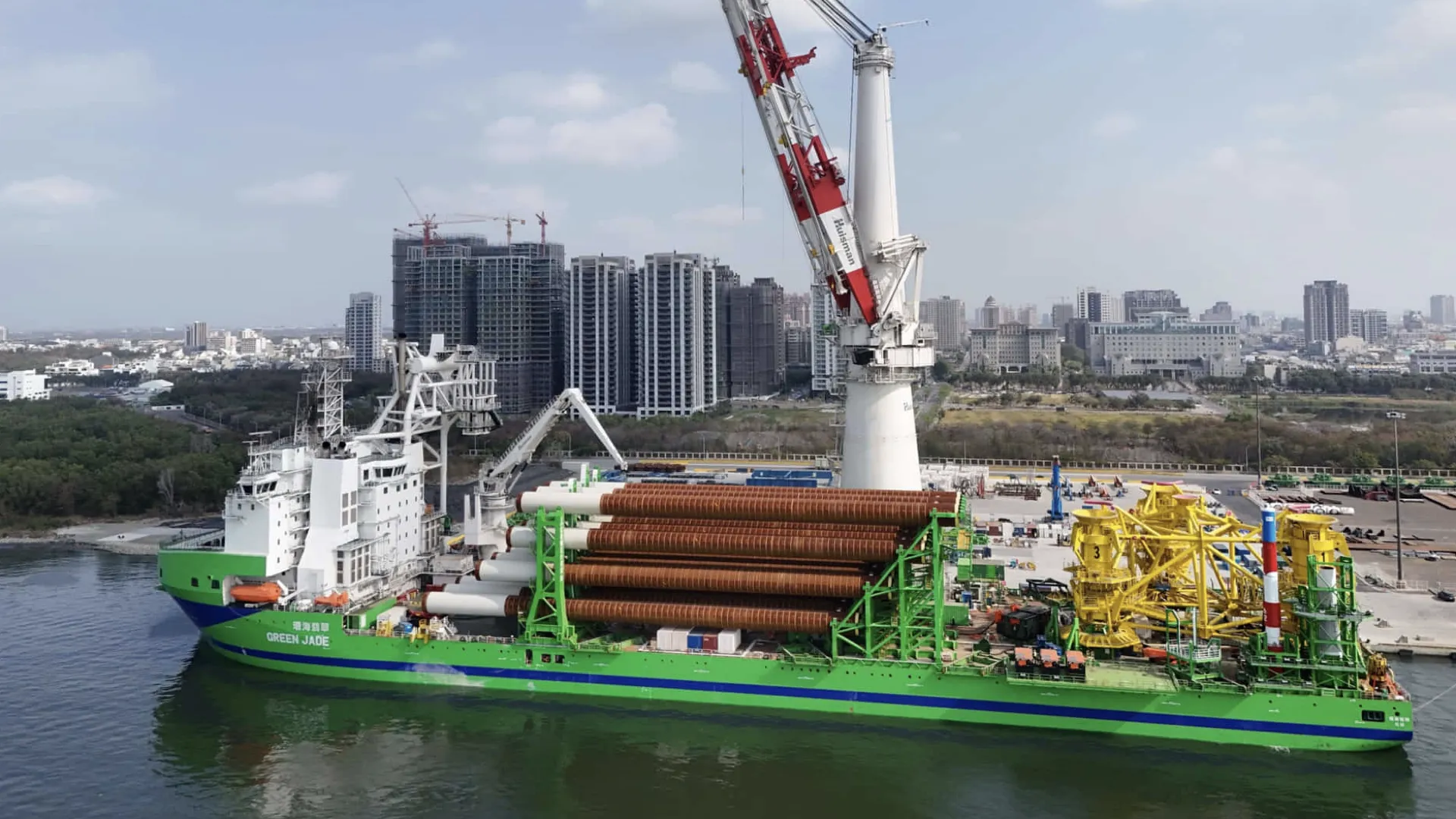
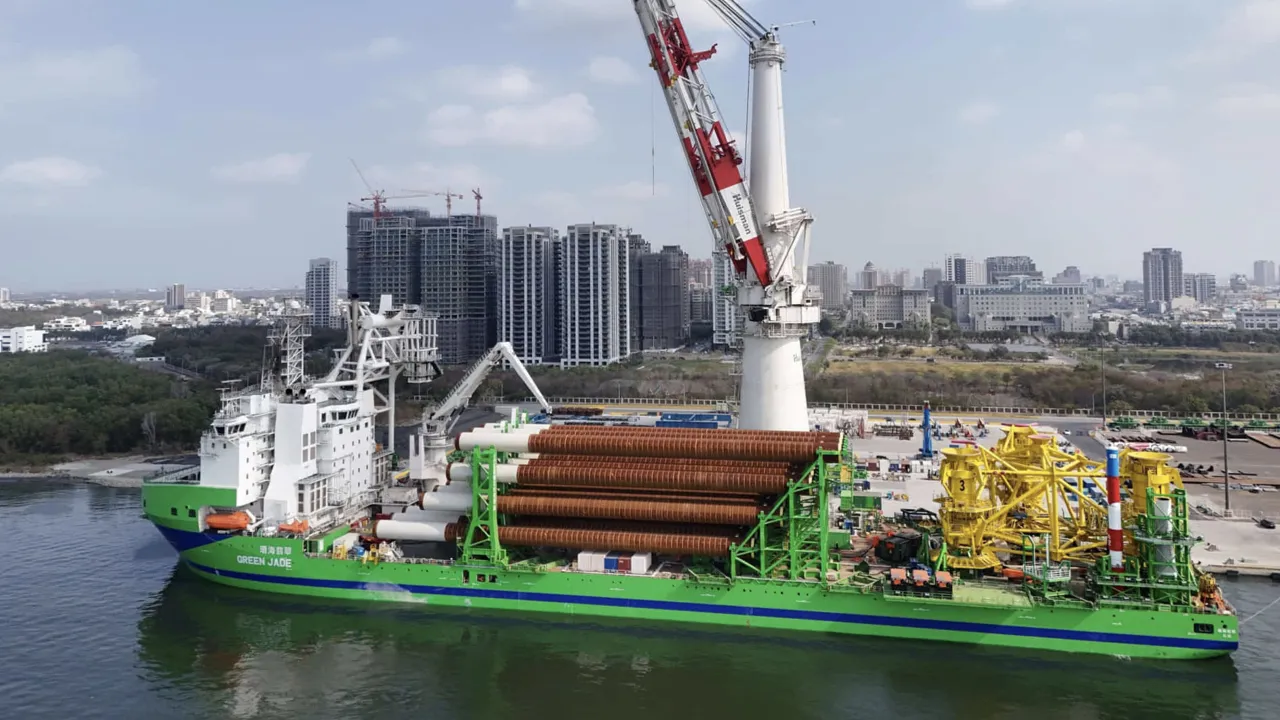
A new and innovative wind turbine installation vessel, named “Green Jade”, was developed by the Belgian dredging company DEME and the Taiwanese shipbuilder CSBC. This sustainable offshore vessel plays a crucial role in offshore wind energy in Taiwan. In addition to a crane capacity of 4,000 tons and DP3 technology for optimal stability and precision, this vessel is equipped with eight ORC-based waste heat recovery systems, supplied by our partner.
Design Criteria
This ship was designed with a strong focus on reducing CO2 emissions to meet stricter shipping regulations, such as the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII). This indicator measures carbon intensity per ton-kilometer and encourages more efficient solutions. Moreover, the design helps significantly reduce the project’s ecological footprint. Thanks to the waste heat recovery systems (WHRS), heat that would normally be lost through exhaust gases is efficiently recovered and converted into electricity. This increases operational efficiency, promotes sustainability, and supports an energy-efficient propulsion system.
Challenges and Solutions
One challenge in efficiently recovering and utilizing waste heat from the engines was ensuring that the systems function effectively under varying load levels. Thanks to the flexible design of the ORC-based technology, they can adapt optimally to these fluctuations. This is crucial for the dynamic operating conditions on board.
Of the four installed dual-fuel engines, each is equipped with two waste heat recovery systems. When all engines are running, these systems collectively generate more than 500 kW (net) of electricity from the engines’ waste heat. This not only increases the vessel’s energy efficiency but also significantly contributes to reducing CO2 emissions.
Looking for more inspiration? Visit our page showcasing featured projects to explore concrete examples of how ships can operate more efficiently and sustainably, not only with waste heat recovery systems but also through other cutting-edge technologies.